Brain Seeing . Geons . Canonical Perspective
- Apr 21, 2018
- 4 min read
Updated: May 8, 2018

How do you think? How do you decide? what initiates you to purchase, like or select any particular product or merchandise.
Do we ever try to understand what kind of aesthetics ,colour palette,silhouettes ,form , texture etc grabs our attention.There is usually two kind of systems thinking fast and thinking slow, I am going to talk about how to design for both set of systems. We take mental models how the world works and apply them into new situations. All of our past experience helps us to make choices for the future. Author Joe Leech places the example of the atm card so accurately , how our brain processes the order that we have been following. Like the usual order would be "enter card" , " enter pin ", "select amount", "remove card" and then "get cash " but if you go to Argentina and try to withdraw money the pattern changes " enter card" , " enter pin", " select amount ", " get cash" and finally comes " remove card". This twist in the pattern leads to the mishap of forgetting the atm card in the atm and leaving the atm only with cash. This example is quite similar to banking with HDFC atms in Indian context.
What we see ! what we analyse . Our brain processes the data majorly by seeing and further interpreting. what our eyes are perceiving is one half of the entire story, the rest half is about what our brain is trying to perceive or "see" --- We can call it " brain seeing".
Peripheral vision is more important than central vision.
First of all we need to clearly understand what is meant by peripheral vision -- it is simply the ability to see objects and movements outside of the direct line of vision , it is the work of the rods and nerve cell located outside the macula( the center of the retina). New Research from the Kansas State university shows that peripheral vision is more important in understanding the subject around us. Adam Larson and Lester Loschky (2009) two famous psychologist showed people picture of common household scenes for a very short amount of time putting hindrance in two segments of the picture. They repeated this activity twice where in first case they put a grey filter on center part of the image and for the second time they put a filter in the peripheral part of the image. People failed to decipher the picture which had a grey filter in the periphery and the one with the grey filter at the center was still comparatively recognizable. They tried obscuring different amounts of the photo. They analysed that central vision is the most critical for specific object recognition, but peripheral vision is for getting the gist of a scene.
Have you ever pondered why it is disturbing when something is incessantly blinking on your computer screen ?
We can't help but notice the movement by our peripheral vision, it is extremely irritating if i am reading a text on the screen and something pops from the side of the screen. This is what the advertisers do these days to grab the attention of the user.
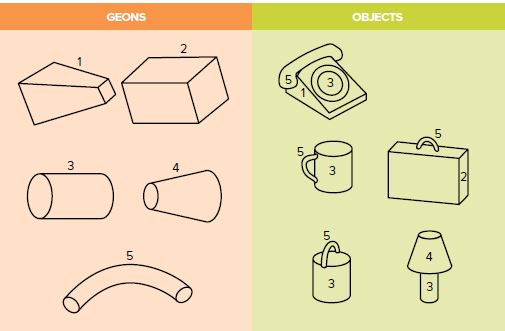
The Geon theory of Object Recognition
We tend to identify objects by recognizing patterns. There has been multiple theories of identifying objects like our brain stores millions of objects in its memory bank, when you see an object , you compare it with all the items in your memory bank until you find the one that matches.
Latest research states facts which supports the idea of geometric outlines. when we are looking at shapes we look at the geometrical outlines and trace out basic shapes to identify objects. Irving Biederman proposed the ideas of Geons in 1985, it clearly states that there are 24 basic shapes that we recognize , they for the basic building blocks of the objects/ forms we tend to identify.
Understanding canonical perspective
If we are asked to draw a mug, we would straight way draw a mug as shown in the figure below., from a perspective slightly above the cup looking down and offset a little to the right or the left. This is called canonical perspective. Very few people would draw the mug from a bird eye view.
Researcher Stephen Palmer (1981) undertook a small research on how people draw things. They were asked to draw various objects like cup, bottles , animals etc, and most people quickly doodle the side view of the objects or beings. The silhouettes of a particular thing or animal we draw is how exactly our brain registers it while viewing it.
These kind of different perspectives helps in understanding the user behavior. the more we start valuing the user understanding the more our products will make a difference in front of the audience. To design and add value to our designed product we need to keep focusing on the users psychology.
References
IDEO, 2015. The Field Guide to Human-Centered Design. 1st Edition ed. Canada: s.n.
IDEO, B., 2015. The Little Book of Design Research Ethics. 1st edition ed. s.l.:s.n.
Leech, J., n.d. A pocket guide Psychology for Designers. v1-5 ed. s.l.:MRJOE PRESS, 2016.
Patton, b. J., 2014. User Story Mapping. 1st ed. Florida: O’Reilly Media.
Weinschenk., S., 2012. 100 Things Every Designer Needs to Know About People. 1st ed. Berkeley, California.: New Riders.
























Comments